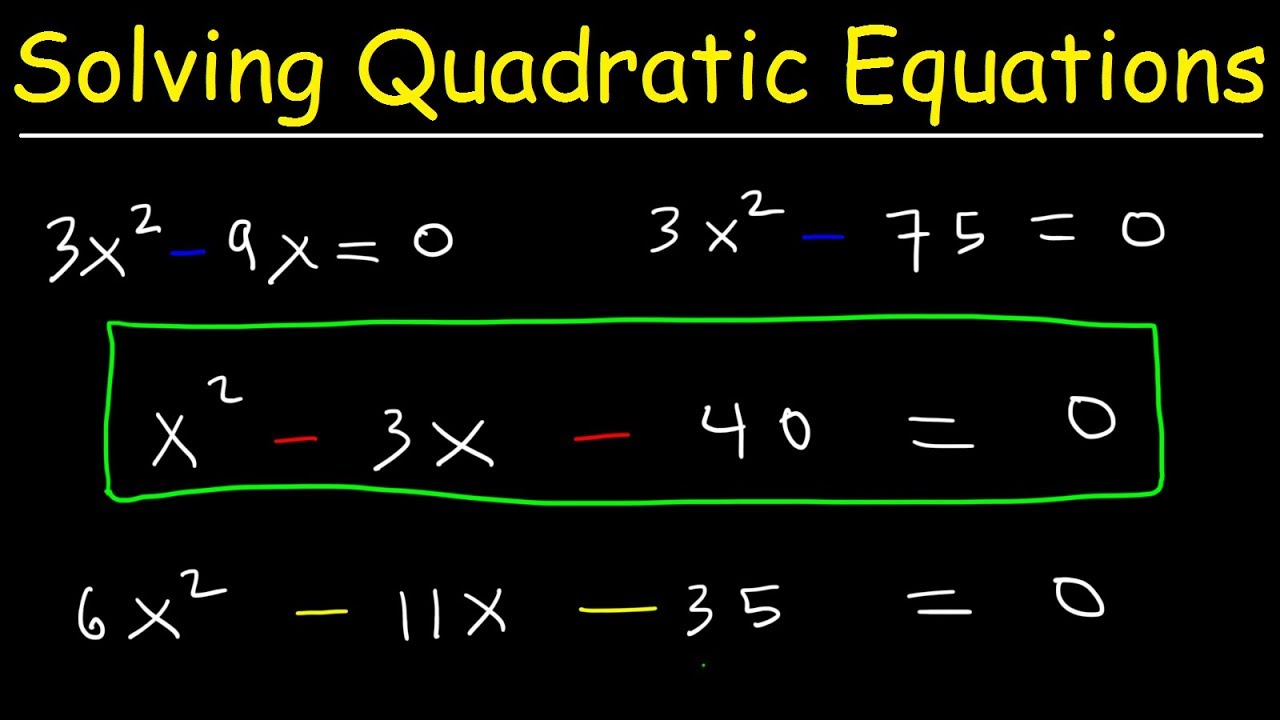
What are Quadratics?
A quadratic is a mathematical expression that can be written in the form of ax^2 + bx + c = 0. Quadratics are usually solved by factoring, which is a process of rewriting the expression in such a way that it can be easily solved. For example, if we have the expression x^2 + 5x + 6 = 0, we can factor it as (x+3)(x+2)=0. This gives us two solutions, x=-3 and x=-2.
How to Factor and Solve Quadratics
To factor and solve quadratics, there are a few different methods you can use. The most common method is to factor the quadratic equation into two linear equations. This can be done by using the Quadratic Formula, or by factoring the equation by grouping.
Once the equation has been factored, you can then solve each linear equation to find the roots of the quadratic equation. You can also use the Quadratic Formula to directly find the roots of the equation without having to factor it first.
If you’re not sure how to factor a quadratic equation, don’t worry! There are plenty of resources available to help you out, including online calculators and step-by-step guides. Once you understand how to factor and solve quadratics, you’ll be able to confidently tackle any math problem that comes your way.
How to Solve Quadratics
To solve a quadratic, one needs to first factor the expression. This can be done by finding two numbers that multiply to give the coefficient of x^2 (a), and add to give the coefficient of x (b). These two numbers are called the factors of b. Once the expression is factored, one can use the zero product property to set each factor equal to zero and solve for x.
Quadratic Formula
The quadratic equation is a mathematical formula used to calculate the roots of a quadratic polynomial. A quadratic polynomial is a polynomial with two terms, such as x^2 + 5x + 6. The quadratic formula is used to solve for the value of x in the equation.
The quadratic equation can be written in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and x is an unknown. To solve for x, we use the following formula:
x = (-b +/- sqrt(b^2 – 4ac)) / (2a)
Where sqrt() represents the square root function. The plus or minus sign in the formula indicates that there are two possible values for x; one value when we take the plus sign and one value when we take the minus sign. In other words, there are two possible solutions to the quadratic equation:
x = (-b + sqrt(b^2 – 4ac)) / (2a) OR x = (-b – sqrt(b^2 – 4ac)) / (2a)
To use the quadratic equation, we first need to identify the values of a, b, and c in our equation. We then plug these values into the formula and solve for x. Let’s look at an example:
Conclusion
To sum it up, in order to factor and solve quadratics, you need to find two numbers that multiply to equal the coefficient of x squared and add up to equal the coefficient of x. Once you have those numbers, you can put them in parentheses with one on each side of the equation and then use the distributive property to simplify. After that, all you have to do is solve for x like you would any other linear equation. We hope this article has helped clear up any confusion you may have had about factoring and solving quadratics.